Anti-inflammatory diets have become increasingly popular in recent years as more research has linked chronic inflammation to a variety of health conditions, including hormonal imbalances, heart disease, cancer, arthritis, and Alzheimer’s disease. Inflammation is a natural response of the body’s immune system to injury or infection, but when it becomes chronic, it can lead to the development of chronic diseases. An anti-inflammatory diet is designed to reduce the level of inflammation in the body by focusing on nutrient-dense, whole foods, and avoiding foods that are known to promote inflammation.
In this article, I will explore the principles of an anti-inflammatory diet, as well as some specific foods for managing chronic inflammation and improving overall health.
What Is An Anti-Inflammatory Diet?
An anti-inflammatory diet is a type of dietary pattern that is designed to reduce inflammation in the body and promote overall health by providing the body with the necessary nutrients.
An anti-inflammatory diet focuses on consuming whole, unprocessed foods that are rich in nutrients, while avoiding foods that can trigger inflammation in the body. Some specific foods and nutrients that may have anti-inflammatory properties include omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and certain phytochemicals.
What Are The Benefits Of An Anti-Inflammatory Diet?
The benefits of an anti-inflammatory diet includes
- Lowered risk of developing chronic illnesses like diabetes, cancer, and heart disease
- Improved overall health and vitality
- Protection against chronic pain and inflammation
- Improved hormonal health
- Better digestion and gut health
- Improved brain health
- Improved skin health
- Enhanced immune function
- Better overall physical and emotional well-being
- Lowered the risk for incidence of certain cancers
- Reduced symptoms of autoimmune diseases.
What Are the Main Principles of an Anti-inflammatory Diet?
The principles of an anti-inflammatory diet include:
- Eating a variety of fruits and vegetables, which are high in antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds.
- Consuming healthy fats, such as olive oil, avocado, and fatty fish, which can help reduce inflammation.
- Limiting or cutting down processed foods, sugar, trans fats, and refined carbohydrates, which can cause inflammation in the body.
- Eating moderate amounts of lean protein, such as chicken, fish, and legumes.
- Incorporating herbs and spices, such as turmeric, ginger, and garlic, which have anti-inflammatory properties.
- Drinking plenty of water and green tea, which can help flush out toxins and reduce inflammation.
- Minimizing alcohol and caffeine intake, as they can increase inflammation in the body.
- Getting enough sleep and exercise, which can help reduce inflammation and improve overall health.
What Are Some Foods to Include In an Anti-Inflammatory Diet
Here are mentioned some foods you should include as part of an anti-inflammatory diet.
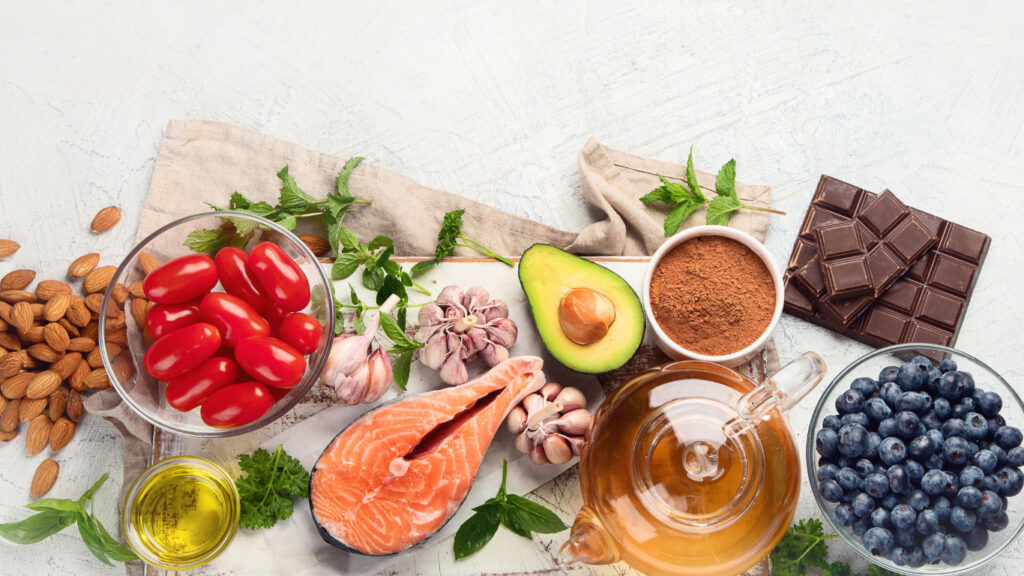
- Berries: these small fruits are high in fiber, vitamins, and minerals and come in many varieties such as strawberries, blueberries, raspberries, and blackberries, all working to reduce inflammation. Berries are high in antioxidants called anthocyanins, which have anti-inflammatory effects that may reduce the risk of disease. Studies have shown that consuming blueberries and strawberries can increase natural killer cells and lower inflammation markers associated with heart disease.
- Fatty fish: Fatty fish such as salmon, sardines, herring, mackerel, and anchovies are good sources of protein and long-chain omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA, which have anti-inflammatory effects that can help reduce the risk of metabolic syndrome, heart disease, diabetes, and kidney disease. Some studies have found that consuming salmon or EPA and DHA supplements can lead to reductions in the inflammatory marker CRP.
- Broccoli: Broccoli is a highly nutritious cruciferous vegetable that has been linked to a decreased risk of heart disease and cancer. This may be due to its anti-inflammatory properties, which are attributed to the antioxidant sulforaphane, which can decrease inflammation by reducing levels of cytokines and nuclear factor kappa B.
- Avocados: Avocados are nutrient-rich fruits that contain potassium, magnesium, fiber, and heart-healthy monounsaturated fats. They also contain carotenoids, tocopherols, which are linked to a reduced risk of cancer. Additionally, they contain a compound that may reduce inflammation in newly forming skin cells. Studies have shown that consuming avocado for 12 weeks can reduce inflammatory markers interleukin 1 beta (IL-1β) and CRP in people with excess weight.
- Green tea: Green tea is considered a healthy beverage with research showing it is associated with a reduced risk of heart disease, cancer, Alzheimer’s disease, obesity and other conditions. This is due to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, particularly the substance called epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) which has the ability to inhibit inflammation by reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and injury to the fatty acids in cells.
- Peppers: Bell peppers and chili peppers are rich in vitamin C and antioxidants that have anti-inflammatory properties. Bell peppers also contain the antioxidant quercetin, which may help reduce inflammation related to chronic diseases like diabetes. Chili peppers contain sinapic acid and ferulic acid, which may help reduce inflammation and support healthy aging.
- Mushrooms: Mushrooms are a low-calorie food that are rich in selenium, copper, and B vitamins. They also contain antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds, such as phenols. Some mushroom varieties like lion’s mane may have potential anti-inflammatory effects related to obesity. However, cooking mushrooms can reduce anti-inflammatory compounds significantly, so it may be best to consume them raw or lightly cooked.
- Grapes: Grapes contain anthocyanins and resveratrol, antioxidants that reduce inflammation and may decrease the risk of several diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, obesity, Alzheimer’s, and eye disorders. Studies have also shown that resveratrol can protect the heart against inflammation. One study found that consuming 50mg of resveratrol daily for 3 months decrease the inflammatory markers in people with heart failure. Another study found that eating grape extract daily increases the levels of adiponectin which is associated with weight gain and increased risk of cancer.
- Turmeric: Curcumin, a potent anti-inflammatory molecule, is present in the spice turmeric. Research has shown that turmeric can reduce inflammation related to various diseases, including arthritis and diabetes. To experience a noticeable effect, it may be necessary to take supplements containing isolated curcumin rather than consuming turmeric alone. Curcumin supplements are often combined with piperine to boost absorption, but more research is needed to understand the dosage effects on inflammatory markers.
- Extra Virgin Olive Oil: Extra virgin olive oil is a healthy fat with numerous health benefits, including a reduced risk of heart disease, brain cancer, and other serious health conditions. Studies have shown that consuming it may decrease CRP and other inflammatory markers. It contains the antioxidant oleocanthal which has anti-inflammatory effects similar to ibuprofen, but it’s more beneficial than refined olive oil.
- Dark Chocolate: Dark chocolate is rich in antioxidants and flavanols which can reduce inflammation and improve vascular function. Studies have linked it to a reduced risk of disease and healthier aging. To maximize the anti-inflammatory benefits, choose dark chocolate that contains at least 70% cocoa.
- Tomatoes: Vitamin C, potassium, and lycopene, an antioxidant with potent anti-inflammatory qualities, are all abundant in tomatoes. Lycopene is quite supportive for reducing pro-inflammatory substances associated to certain cancer types. Cooking tomatoes in olive oil can help increase absorption of lycopene because it is a carotenoid that is better absorbed with a source of fat.
- Cherries: Cherries are high in antioxidants, such as anthocyanins and catechins, which have anti-inflammatory properties. Tart cherries have been studied more extensively than other varieties, and studies have shown that consuming tart cherry juice can lower levels of the inflammatory marker CRP. However, more research is needed to understand how cherries can help reduce inflammation.
Foods to Avoid In an Anti-Inflammatory Diet
An anti-inflammatory diet typically involves avoiding
- Processed foods and snacks, such as chips, crackers, and cookies.
- Refined carbohydrates like white bread and pasta.
- Fried foods including doughnuts, fried chicken, and french fries.
- Sweetened drinks including processed juice and soda.
- Trans fats like shortening and margarine.
- High omega-6 vegetable oils, such as soybean oil, corn oil, and sunflower oil.
- Red processed meats, such as bacon and deli meats.
- Dairy products, especially those that saturated fat-rich.
- Alcohol, in excessive amounts.
- Gluten, if you are gluten intolerant.
- Artificial sweeteners and additives.
The Bottom Line
An anti-inflammatory diet is a type of dietary pattern that aims to reduce inflammation in the body by providing the body with necessary nutrients and avoiding foods that can trigger inflammation.
It focuses on consuming whole, unprocessed foods that are high in nutrients, such as fruits and vegetables, healthy fats, lean proteins, and herbs and spices.
The benefits of an anti-inflammatory diet include reducing the risk of chronic diseases, improving overall health, weight management, and better digestion and gut health.
Some foods to include in an anti-inflammatory diet include berries, fatty fish, broccoli, avocados, green tea, peppers, and mushrooms.
It is also important to limit processed foods, sugar, trans fats, and refined carbohydrates, and to minimize alcohol and caffeine intake.
Additionally, getting enough sleep and exercise is also important for reducing inflammation and improving overall health.
References
Grandl G, Wolfrum C. Hemostasis, endothelial stress, inflammation, and the metabolic syndrome. Semin Immunopathol. 2018 Feb;40(2):215-224. doi: 10.1007/s00281-017-0666-5. Epub 2017 Dec 5. PMID: 29209827; PMCID: PMC5809518.